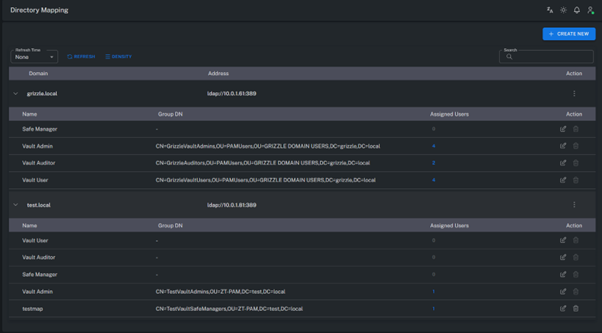
Directory Mapping
Directory Mapping enables integration between your organization’s Active Directory (AD) infrastructure and the Grizzle ZT-PAM system.
Through this integration, Active Directory users and groups are automatically reflected in the PAM environment, allowing centralized identity management.
By defining your Active Directory server within the PAM system, your AD groups can be mapped and synchronized.
Multiple AD environments can be managed and synchronized within the same system.
Synchronization Features
Active Directory synchronization runs automatically based on the intervals defined in the General Settings page.
As a result, user additions, deletions, or group updates made in AD are automatically reflected in the PAM system.
Note: Different domain or forest structures can be defined separately, enabling support for multi-domain Active Directory integration.
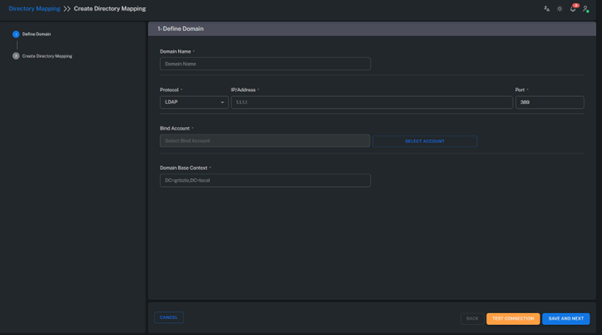
Create Directory Mapping
Used to create a new Directory Mapping definition.
At this stage, Active Directory connection information and configuration parameters are entered.
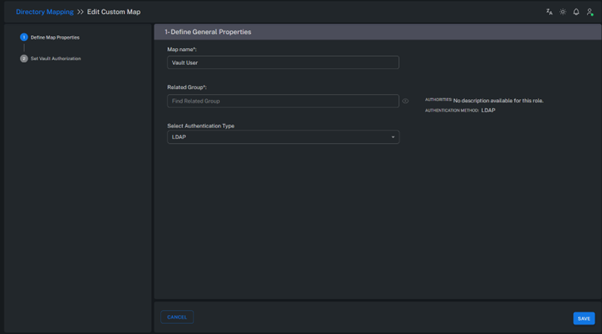
1. Define Mapping Information
Provide a descriptive Mapping Name for the mapping process.
This name helps distinguish and manage multiple AD environments efficiently.
2. View AD Groups
After completing the mapping process, AD groups and users can be viewed.
The number of synchronized groups and users is displayed in this section.
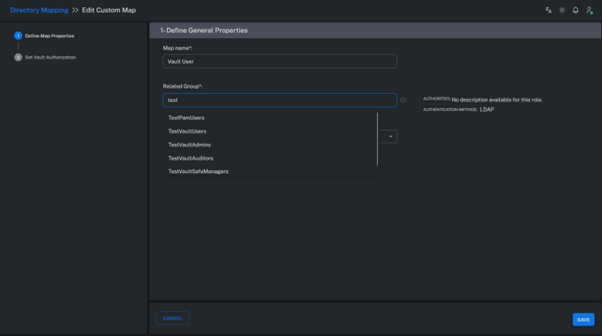
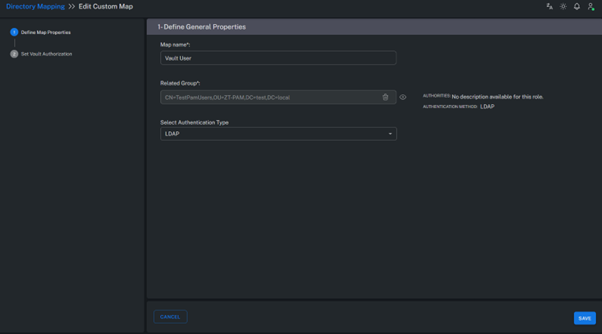
3. Select Related Groups
The Related Groups field specifies which Active Directory groups will be utilized within the PAM system.
Only the groups selected here will be imported and synchronized into the platform.
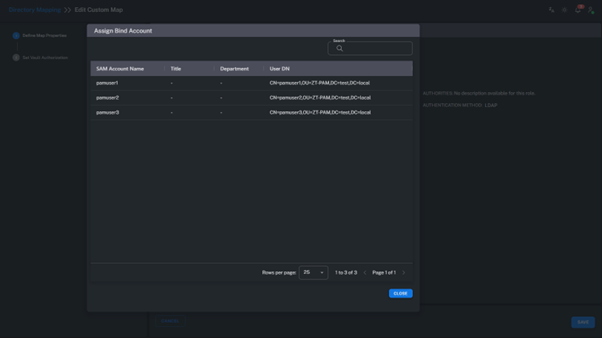
4. View User Details
Once a group is selected, the users belonging to that group are listed in detail.
Summary
Directory Mapping is a critical component that enables seamless integration between Grizzle ZT-PAM and Active Directory.
Through this feature:
- AD user and group information is automatically synchronized with the PAM environment,
- Identity management is centralized,
- Authorization processes align directly with the AD structure,
- Multi-domain and forest environments can be integrated with flexibility.
This functionality provides centralized, secure, and scalable access management—especially valuable in large enterprise environments.